TEST PLAN in Software Testing (Example)
⚡ Smart Summary
A Test Plan is a comprehensive document outlining the scope, objectives, resources, and schedule for software testing, ensuring systematic and controlled validation of application quality. It serves as a foundational blueprint guiding all testing activities with clarity and precision.

Test Plan
A Test Plan is a detailed document that describes the test strategy, objectives, schedule, estimation, deliverables, and resources required to perform testing for a software product. A Test Plan helps us determine the effort needed to validate the quality of the application under test. The test plan serves as a blueprint to conduct software testing activities as a defined process, which is minutely monitored and controlled by the test manager.
As per the ISTQB definition: “Test Plan is A document describing the scope, approach, resources, and schedule of intended test activities.”
Let’s start with the following Test Plan example/scenario: In a meeting, you want to discuss the Test Plan with the team members, but they are not interested.
In such a case, what will you do? Select your answer as shown in the following figure.
A) I am the Manager, and I do everything as I said
B) OK, let me explain why we need a Test Plan
Incorrect
As a Test Manager, you must explain them the importance of Test Plan rather than force the team to do what you want.
Correct
As a Test Manager, you must explain them the importance of Test Plan rather than force the team to do what you want.
👉 Enroll for Free Live Software Testing Project
What is the Importance of a Test Plan?
Making a Test Plan document has multiple benefits.
- Help people outside the test team, such as developers, business managers, and customers, understand the details of testing.
- Test Plan guides our thinking. It is like a rule book, which needs to be followed.
- Important aspects like test estimation, test scope, Test Strategy are documented in Test Plan, so it can be reviewed by the Management Team and reused for other projects.
Types of Test Plans
There are three main types of Test Plans in software testing.
- Master Test Plan: A high-level document outlining the overall testing strategy, scope, resources, and schedule for all test levels. It serves as the project’s master roadmap.
- Level-Specific Test Plan: Focuses on particular testing levels such as unit, integration, system, or acceptance testing. Each plan details the approach, environment, and deliverables for that level.
- Type-Specific Test Plan: Targets specialized testing types like performance, security, usability, or automation testing. It defines tools, techniques, and criteria unique to that test type.
Together, these test plans ensure comprehensive coverage, align testing objectives with project goals, and improve coordination across teams for higher software quality.
How to write a Test Plan
You already know that making a Test Plan is the most important task of the Test Management Process. Follow the seven steps below to create a test plan as per IEEE 829
- Analyze the product
- Design the Test Strategy
- Define the Test Objectives
- Define Test Criteria
- Resource Planning
- Plan Test Environment
- Schedule & Estimation
- Determine Test Deliverables
Step 1) Analyze the product
How can you test a product without any information about it? The answer is Impossible. You must learn a product thoroughly before testing it.
The product under test is the Guru99 banking website. You should research clients and the end users to know their needs and expectations from the application.
- Who will use the website?
- What is it used for?
- How will it work?
- What software/ hardware does the product use?
You can use the following approach to analyze the site.
Now let’s apply above knowledge to a real product: Analyze the banking website https://demo.guru99.com/V4.
You should take a look around this website and also review product documentation. Review of product documentation helps you to understand all the features of the website as well as how to use it. If you are unclear on any items, you might interview customer, developer, designer to get more information.
Step 2) Develop Test Strategy
Test Strategy is a critical step in making a Test Plan in Software Testing. A Test Strategy document is a high-level document, which is usually developed by the Test Manager. This document defines:
- The project’s testing objectives and the means to achieve them
- Determines testing effort and costs
Back to your project, you need to develop a Test Strategy for testing that banking website. You should follow the steps below.
Step 2.1) Define Scope of Testing
Before the start of any test activity, the scope of the testing should be known. You must think hard about it.
- The components of the system to be tested (hardware, software, middleware, etc.) are defined as “in scope“
- The components of the system that will not be tested also need to be clearly defined as being “out of scope.”
Defining the scope of your testing project is very important for all stakeholders. A precise scope helps you.
- Give everyone confidence & accurate information about the testing you are doing.
- All project members will have a clear understanding of what is tested and what is not.
How do you determine the scope of your project?
To determine scope, you must –
- Precise customer requirement
- Project Budget
- Product Specification
- Skills & talent of your test team
Now, it should clearly define the “in scope” and “out of scope” of the testing.
- As the software requirement specs, the project Guru99 Bank only focus on testing all the functions and external interface of website Guru99 Bank (in scope testing)
- Nonfunctional testing such as stress, performance or logical database will not be tested. (out of scope)
Problem Scenario
The customer wants you to test his API. But the project budget does not permit doing so. In such a case, what will you do?
Well, in such a case, you need to convince the customer that Api Testing is extra work and will consume significant resources. Give him data supporting your facts. Tell him that if Api Testing is included in scope, the budget will increase by XYZ amount.
The customer agrees, and accordingly, the new scopes, out-of-scope items are
- In-scope items: Functional Testing, Api Testing
- Out of scope items: Database Testing, hardware & any other external interfaces
Step 2.2) Identify Testing Type
A Testing Type is a standard test procedure that gives an expected test outcome.
Each testing type is formulated to identify a specific type of product bugs. But, all Testing Types are aimed at achieving one common goal: “Early detection of all the defects before releasing the product to the customer”
The commonly used testing types are described as follows in the figure
There are tons of Testing Types for testing a software product. Your team cannot put in enough effort to handle all kinds of testing. As Test Manager, you must set the priority of the Testing Types
- Which Testing Types should be focused on for web application testing?
- Which Testing Types should be ignored for saving cost?
Step 2.3) Document Risk & Issues
Risk is a future uncertain event with a probability of occurrence and a potential for loss. When the risk actually happens, it becomes the ‘issue’.
In the article Risk Analysis and Solution, you have already learned about the ‘Risk’ analysis in detail and identified potential risks in the project.
In the QA Test Plan, you will document those risks
| Risk | Mitigation |
|---|---|
| Team members lack the required skills for website testing. | Plan a training course to skill up your members |
| The project schedule is too tight; it’s hard to complete this project on time | Set Test Priority for each of the test activities. |
| The Test Manager has poor management skills | Plan leadership training for the manager |
| A lack of cooperation negatively affects your employees’ productivity | Encourage each team member in their task, and inspire them to greater efforts. |
| Wrong budget estimate and cost overruns | Establish the scope before beginning work, pay a lot of attention to project planning, and constantly track and measure the progress |
Step 2.4) Create Test Logistics
In Test Logistics, the Test Manager should answer the following questions:
- Who will test?
- When will the test occur?
Who will test?
You may not know the exact names of the testers who will test, but the type of tester can be defined.
To select the right member for a specified task, you have to consider whether their skill are qualified for the task or not, and also estimate the project budget. Selecting the wrong member for the task may cause the project to fail or be delayed.
A person having the following skills is ideal for performing software testing:
- Ability to understand the customer’s point of view
- Strong desire for quality
- Attention to detail
- Good cooperation
In your project, the member who will take charge of the test execution is the tester. Based on the project budget, you can choose an in-house or outsourced member as the tester.
When will the test occur?
Test activities must be matched with associated development activities.
You will start to test when you have all the required items shown in the following figure.
Step 3) Define Test Objective
The Test Objective is the overall goal and achievement of the test execution. The objective of the testing is to find as many software defects as possible; ensure that the software under test is bug-free before release.
To define the test objectives, you should do the following two steps
- List all the software features (functionality, performance, GUI…) that may need to be tested.
- Define the target or the goal of the test based on the above features
Let’s apply these steps to find the test objective of your Guru99 Bank testing project
You can choose the ‘TOP-DOWN’ method to find the website’s features that may need to be tested. In this method, you break down the application under test into components and sub-components.
In the previous topic, you have already analyzed the requirement specs and walked through the website, so you can create a Mind-Map to find the website features as follows:
This figure shows all the features that the Guru99 website may have.
Based on the above features, you can define the Test Objective of the project Guru99 as follows:
- Check whether the website Guru99 functionality(Account, Deposit…) is working as expected without any errors or bugs in the real business environment
- Check that the external interface of the website, such as UI, is working as expected and & meets the customer’s needs
- Verify the usability of the website. Are those functionalities convenient for the user or not?
Step 4) Define Test Criteria
Test Criteria is a standard or rule on which a test procedure or test judgment can be based. There are 2 types of test criteria as follows:
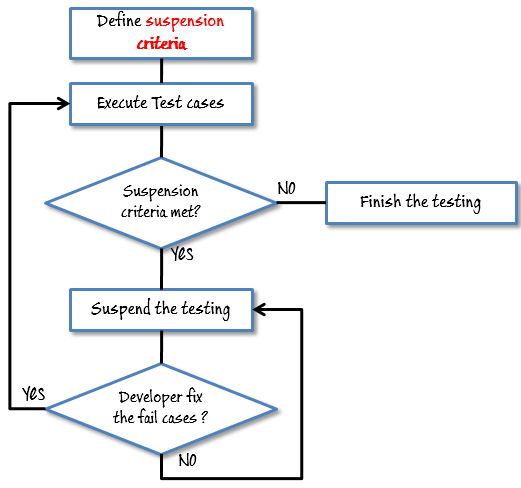
Suspension Criteria
Specify the critical suspension criteria for a test. If the suspension criteria are met during testing, the active test cycle will be suspended until the criteria are resolved.
Test Plan Example: If your team members report that 40% of test cases failed, you should suspend testing until the development team fixes all the failed cases.
Exit Criteria
It specifies the criteria that denote a successful completion of a test phase. The exit criteria are the targeted results of the test and are necessary before proceeding to the next phase of development. Example: 95% of all critical test cases must pass.
Some methods of defining exit criteria are by specifying a targeted run rate and pass rate.
- Run rate is the ratio between the number of test cases executed and/total test cases of the test specification. For example, the test specification has a total of 120 TCs, but the tester only executed 100 TCs, so the run rate is 100/120 = 0.83 (83%)
- The pass rate is the ratio between the number of test cases passed / test cases executed. For example, in the above 100 TCs executed, there are 80 TCs that passed, so the pass rate is 80/100 = 0.8 (80%)
This data can be retrieved in Test Metric documents.
- Run rate is mandatory to be 100% unless a clear reason is given.
- Pass rate is dependent on project scope, but achieving a high pass rate is a goal.
Test Plan Example:Your Team has already done the test executions. They report the test result to you, and they want you to confirm the Exit Criteria.
In the above case, the Run rate is mandatory and is 100%, but the test team only completed 90% of the test cases. It means the Run rate is not satisfied, so do NOT confirm the Exit Criteria.
Step 5) Resource Planning
A resource plan is a detailed summary of all types of resources required to complete a project task. Resources could be human, equipment, and materials needed to complete a project.
The resource planning is an important factor of the test planning because it helps in determining the number of resources (employees, equipment…) to be used for the project. Therefore, the Test Manager can make the correct schedule & estimation for the project.
This section represents the recommended resources for your project.
Human Resource
The following table represents various members in your project team
| No. | Member | Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Test Manager | Manage the whole project Define project directions Acquire appropriate resources |
| 2. | Tester | Identifying and describing appropriate test techniques/tools/automation architecture Verify and assess the Test Approach Execute the tests, log results, and report the defects. Tester could be in-sourced or outsourced members, based on the project budget. For the task that requires low skill, I recommend you choose outsourced members to save project cost. |
| 3. | Developer in Test | Implement the test cases, test program, test suite, etc. |
| 4. | Test Administrator | Builds up and ensures Test Environment and assets are managed and maintained Support Tester to use the test environment for test execution |
| 5. | SQA members | Take charge of quality assurance. Check to confirm whether the testing process is meeting the specified requirements |
System Resource
For testing a web application, you should plan the resources as follows:
| No. | Resources | Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Server | Install the web application under test. This includes a separate web server, database server, and application server, if applicable |
| 2. | Test tool | The testing tool is to automate the testing, simulate the user operation, and generate the test results. There are tons of test tools you can use for this project, such as Selenium, QTP, etc. |
| 3. | Network | You need a Network, including LAN and Internet, to simulate the real business and user environment |
| 4. | Computer | The PC that users often use to connect to the web server |
Step 6) Plan Test Environment
What is the Test Environment
A testing environment is a setup of software and hardware on which the testing team is going to execute test cases. The test environment consists of a real business and user environment, as well as physical environments, such as a server and a front-end running environment.
How to set up the Test Environment
Back to your project, how do you set up a test environment for this banking website?
To finish this task, you need strong cooperation between the Test Team and the Development Team.
You should ask the developer some questions to understand the web application under test clearly. Here are some recommended questions. Of course, you can ask the other questions if you need.
- What is the maximum user connections that this website can handle at the same time?
- What are the hardware/software requirements to install this website?
- Does the user’s computer need any particular settings to browse the website?
The following figure describes the test environment of the banking website https://demo.guru99.com/V4
Step 7) Schedule & Estimation
In the article Test estimation, you already used some techniques to estimate the effort to complete the project. Now you should include that estimation as well as the schedule in the Test Planning
In the Test Estimation phase, suppose you break out the whole project into small tasks and add the estimation for each task as follows
| Task | Members | Estimate effort |
|---|---|---|
| Create the test specification | Test Designer | 170 man-hour |
| Perform Test Execution | Tester, Test Administrator | 80 man-hour |
| Test Report | Tester | 10 man-hour |
| Test Delivery | 20 man-hour | |
| Total | 280 man-hour |
Then you create the schedule to complete these tasks.
Making a schedule is a common term in project management. By creating a solid schedule in the Test Planning, the Test Manager can use it as a tool for monitoring the project progress and controlling the cost overruns.
To create the project schedule, the Test Manager needs several types of input as follows:
- Employee and project deadline: The working days, the project deadline, and resource availability are the factors that affect the schedule
- Project estimation: Based on the estimation, the Test Manager knows how long it takes to complete the project. So he can make the appropriate project schedule
- Project Risk: Understanding the risk helps the Test Manager add enough extra time to the project schedule to deal with the risks
Let’s practice with an example:
Suppose the boss wants to complete the project Guru99 in one month, and you have already estimated the effort for each task in Test Estimation. You can create the schedule as follows
Step 8) Test Deliverables
Test Deliverables is a list of all the documents, tools, and other components that have to be developed and maintained in support of the testing effort.
There are different test deliverables at every phase of the software development lifecycle.
Test deliverables are provided before the testing phase.
- Test plans document.
- Test cases documents
- Test Design specifications.
Test deliverables are provided during the testing
- Test Scripts
- Simulators.
- Test Data
- Test Traceability Matrix
- Error logs and execution logs.
Test deliverables are provided after the testing cycle is over.
- Test Results/reports
- Defect Report
- Installation/ Test procedures guidelines
- Release notes
Common Challenges in Test Planning (and Their Solutions)
Effective test planning often faces practical hurdles. Recognizing these challenges and applying proactive solutions ensures smoother execution and higher software quality.
- Unclear Requirements
Challenge: Ambiguous or changing project requirements lead to incomplete test coverage.
Solution: Conduct requirement walkthroughs and maintain a living requirement traceability matrix. - Limited Resources
Challenge: Insufficient tools, time, or skilled testers affect test quality.
Solution: Prioritize critical test cases and leverage automation for repetitive tasks. - Unrealistic Deadlines
Challenge: Tight schedules reduce time for proper test design and execution.
Solution: Use estimation techniques and communicate risks early to stakeholders. - Poor Communication
Challenge: Misalignment between teams causes delays and rework.
Solution: Implement regular sync meetings and shared dashboards for transparency. - Inadequate Risk Management
Challenge: Ignoring potential risks can derail project timelines.
Solution: Identify risks early, maintain a risk log, and plan mitigation strategies.